Spill Disk
概述
Doris's computing layer adopts an MPP (Massively Parallel Processing) architecture, where all computing tasks are completed in the memory of BEs (Backends), and data exchange between BEs is also conducted through memory. Therefore, memory management plays a crucial role in ensuring the stability of queries. According to online query statistics, a significant portion of query errors are related to memory issues. As more and more users migrate tasks such as ETL data processing, multi-table materialized view processing, and complex AdHoc queries to Doris, it is necessary to offload intermediate operation results to disk to enable the execution of queries that require more memory than each query or each node can handle. Specifically, when processing large datasets or executing complex queries, memory consumption can increase rapidly, exceeding the memory limits of a single node or the entire query processing process. Doris alleviates memory pressure by writing intermediate results (such as intermediate states of aggregation, temporary data for sorting, etc.) to disk rather than relying solely on memory to store these data. This approach offers several benefits:
- Scalability: Allows Doris to handle datasets much larger than the memory limit of a single node.
- Stability: Reduces the risk of query failures or system crashes due to insufficient memory.
- Flexibility: Enables users to execute more complex queries without increasing hardware resources.
To avoid triggering OOM (Out of Memory) when requesting memory, Doris has introduced a reserve memory mechanism. The workflow of this mechanism is as follows:
- During execution, Doris estimates the memory size required to process each block and then requests it from a unified memory manager.
- The global memory allocator determines whether the current memory request exceeds the memory limit of the query or the entire process. If it does, the request fails.
- When Doris receives a failure message, it suspends the current query, selects the largest operator for spilling to disk, and resumes query execution after spilling is complete.
Currently, the operators that support spilling include:
- Hash Join operator
- Aggregation operator
- Sort operator
- CTE
When a query triggers spilling, additional disk read/write operations may significantly increase query time. It is recommended to increase the FE Session variable query_timeout. Additionally, spilling can generate significant disk I/O, so it is advisable to configure a separate disk directory or use SSD disks to reduce the impact of query spilling on normal data ingestion or queries. The query spilling feature is currently disabled by default.
##Memory Management Mechanism
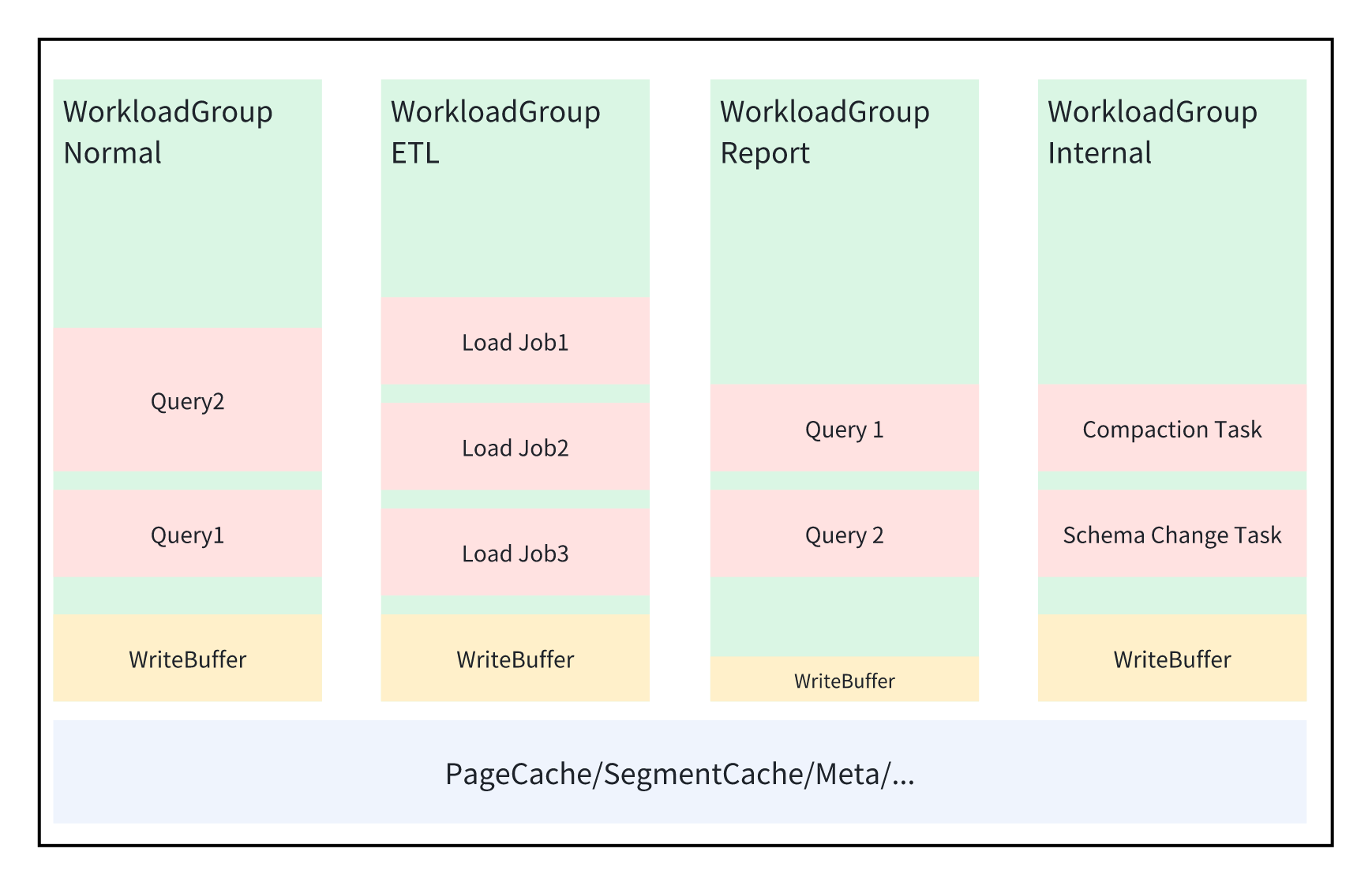
Doris's memory management is divided into three levels: process level, WorkloadGroup level, and Query level.
BE Process Memory Configuration
The memory of the entire BE process is controlled by the mem_limit parameter in be.conf. Once Doris's memory usage exceeds this threshold, Doris cancels the current query that is requesting memory. Additionally, a background task asynchronously kills some queries to release memory or cache. Therefore, Doris's internal management operations (such as spilling to disk, flushing memtable, etc.) need to run when approaching this threshold to avoid reaching it. Once the threshold is reached, to prevent the entire process from experiencing OOM, Doris takes some drastic self-protection measures. When Doris's BE is collocated with other processes (such as Doris FE, Kafka, HDFS), the actual available memory for Doris BE may be significantly less than the user-set mem_limit, causing the internal memory release mechanism to fail and potentially leading to the Doris process being killed by the operating system's OOM Killer. When the Doris process is deployed in K8S or managed by Cgroup, Doris automatically senses the memory configuration of the container.
Workload Group Memory Configuration
- memory_limit,default is 30%. Represents the percentage of memory allocated to the current workload group as a fraction of the entire process memory.
- enable_memory_overcommit, default is true. Indicates whether the memory limit for the current workload group is a hard or soft limit. When this value is true, it means that the memory usage of all tasks within this workload group can exceed the memory_limit. However, when the memory of the entire process is insufficient, to ensure rapid memory reclamation, BE will prioritize canceling queries from workload groups that exceed their limits without waiting for spilling to disk. This is a user-friendly configuration strategy when users are unsure how much memory to allocate to multiple workload groups.
- write_buffer_ratio,default is 20%. Represents the size of the write buffer within the current workload group. To speed up data ingestion, Doris first accumulates data in memory (i.e., constructs a Memtable), sorts it in its entirety when it reaches a certain size, and then writes it to disk. However, accumulating too many Memtables in memory can affect the memory available for normal queries, leading to query cancellation. Therefore, Doris allocates a separate write buffer for each workload group. For workload groups with heavy write operations, a larger write buffer can effectively improve ingestion throughput; for workload groups with more query operations, this value can be reduced.
- low watermark: Default is 75%.
- high watermark: Default is 90%.
Query Memory Management
Static Memory Allocation
The memory used by a query is controlled by the following two parameters:
- exec_mem_limit, representing the maximum memory that a query can use, with a default value of 2GB.
- enable_mem_overcommit, default is true. Indicates whether the memory used by a query can exceed the exec_mem_limit. The default value is true, meaning it can exceed this limit. When the process memory is insufficient, queries that exceed the memory limit will be killed. If set to false, the query's memory usage cannot exceed this limit. When exceeded, spilling to disk or query killing will occur based on user settings. These two parameters must be set by the user in the session variable before query execution and cannot be dynamically modified during execution.
Slot-Based Memory Allocation
In practice, we found that with static memory allocation, users often do not know how much memory to allocate to a query. Therefore, exec_mem_limit is frequently set to half of the entire BE process memory, meaning that the memory used by all queries within the BE cannot exceed half of the process memory. In this scenario, this feature effectively becomes a kind of fuse. When we need to implement more granular policy control based on memory size, such as spilling to disk, this value is too large to rely on for control. Therefore, we have implemented a new slot-based memory limitation method based on workload groups. The principle of this strategy is as follows:
- Each workload group is configured with two parameters by the user: memory_limit and max_concurrency. It is assumed that the memory of the entire BE is divided into max_concurrency slots, with each slot occupying memory_limit / max_concurrency of memory.
- By default, each query occupies one slot during execution. If the user wants a query to use more memory, they need to modify the query_slot_count value.
- Since the total number of slots in a workload group is fixed, increasing query_slot_count means each query occupies more slots, dynamically reducing the number of queries that can run concurrently in the workload group, causing new queries to automatically queue.
The slot_memory_policy for workload groups can have three optional values:
- disabled, the default value, indicating that it is not enabled and the static memory allocation method is used.
- fixed, where the memory that each query can use is calculated as workload group's mem_limit * query_slot_count / max_concurrency.
- dynamic, where the memory that each query can use is calculated as workload group's mem_limit * query_slot_count / sum(running query slots). This mainly overcomes the issue of unused slots in fixed mode. Both fixed and dynamic set hard limits for queries. Once exceeded, spilling to disk or query killing will occur, and these will override the static memory allocation parameters set by the user. Therefore, when setting slot_memory_policy, it is essential to properly configure max_concurrency for the workload group to avoid memory insufficiency issues.
Spilling
Enabling Query Intermediate Result Spilling
BE Configuration Items
spill_storage_root_path=/mnt/disk1/spilltest/doris/be/storage;/mnt/disk2/doris-spill;/mnt/disk3/doris-spill
spill_storage_limit=100%
- spill_storage_root_path: The storage path for query intermediate result spilling files, which defaults to the same as storage_root_path.
- spill_storage_limit: The disk space limit for spilling files. It can be configured with a specific space size (e.g., 100GB, 1TB) or a percentage, with a default of 20%. If spill_storage_root_path is configured with a separate disk, it can be set to 100%. This parameter primarily prevents spilling from occupying too much disk space, impeding normal data storage. After modifying the configuration items, you need to restart BE for them to take effect.
FE Session Variable
set enable_spill=true;
set exec_mem_limit = 10g
set enable_mem_overcommit = false
- enable_spill, indicates whether spilling is enabled for a query.
- exec_mem_limit, represents the maximum memory size used by a query.
- enable_mem_overcommit, indicates whether a query can use memory exceeding the exec_mem_limit.
Workload Group
The default memory_limit for workload groups is 30%, which can be adjusted based on the actual number of workload groups. If there is only one workload group, it can be adjusted to 90%.
alter workload group normal properties ( 'memory_limit'='90%' );
Monitoring Spilling
Audit Logs
The FE audit log has added the SpillWriteBytesToLocalStorage and SpillReadBytesFromLocalStorage fields, representing the total amount of data written to and read from local storage during spilling, respectively.
SpillWriteBytesToLocalStorage=503412182|SpillReadBytesFromLocalStorage=503412182
Profile
If spilling is triggered during a query, some Spill-prefixed counters are added to the Query Profile to mark and count spilling-related activities. Taking HashJoin's Build HashTable as an example, you can see the following counters:
PARTITIONED_HASH_JOIN_SINK_OPERATOR (id=4 , nereids_id=179):(ExecTime: 6sec351ms)
- Spilled: true
- CloseTime: 528ns
- ExecTime: 6sec351ms
- InitTime: 5.751us
- InputRows: 6.001215M (6001215)
- MemoryUsage: 0.00
- MemoryUsagePeak: 554.42 MB
- MemoryUsageReserved: 1024.00 KB
- OpenTime: 2.267ms
- PendingFinishDependency: 0ns
- SpillBuildTime: 2sec437ms
- SpillInMemRow: 0
- SpillMaxRowsOfPartition: 68.569K (68569)
- SpillMinRowsOfPartition: 67.455K (67455)
- SpillPartitionShuffleTime: 836.302ms
- SpillPartitionTime: 131.839ms
- SpillTotalTime: 5sec563ms
- SpillWriteBlockBytes: 714.13 MB
- SpillWriteBlockCount: 1.344K (1344)
- SpillWriteFileBytes: 244.40 MB
- SpillWriteFileTime: 350.754ms
- SpillWriteFileTotalCount: 32
- SpillWriteRows: 6.001215M (6001215)
- SpillWriteSerializeBlockTime: 4sec378ms
- SpillWriteTaskCount: 417
- SpillWriteTaskWaitInQueueCount: 0
- SpillWriteTaskWaitInQueueTime: 8.731ms
- SpillWriteTime: 5sec549ms
System Tables
backend_active_tasks
The SPILL_WRITE_BYTES_TO_LOCAL_STORAGE and SPILL_READ_BYTES_FROM_LOCAL_STORAGE fields have been added, representing the total amount of data currently being written to and read from local storage for intermediate results during a query.
mysql [information_schema]>select * from backend_active_tasks;
+-------+------------+-------------------+-----------------------------------+--------------+------------------+-----------+------------+----------------------+---------------------------+--------------------+-------------------+------------+------------------------------------+-------------------------------------+
| BE_ID | FE_HOST | WORKLOAD_GROUP_ID | QUERY_ID | TASK_TIME_MS | TASK_CPU_TIME_MS | SCAN_ROWS | SCAN_BYTES | BE_PEAK_MEMORY_BYTES | CURRENT_USED_MEMORY_BYTES | SHUFFLE_SEND_BYTES | SHUFFLE_SEND_ROWS | QUERY_TYPE | SPILL_WRITE_BYTES_TO_LOCAL_STORAGE | SPILL_READ_BYTES_FROM_LOCAL_STORAGE |
+-------+------------+-------------------+-----------------------------------+--------------+------------------+-----------+------------+----------------------+---------------------------+--------------------+-------------------+------------+------------------------------------+-------------------------------------+
| 10009 | 10.16.10.8 | 1 | 6f08c74afbd44fff-9af951270933842d | 13612 | 11025 | 12002430 | 1960955904 | 733243057 | 70113260 | 0 | 0 | SELECT | 508110119 | 26383070 |
| 10009 | 10.16.10.8 | 1 | 871d643b87bf447b-865eb799403bec96 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | SELECT | 0 | 0 |
+-------+------------+-------------------+-----------------------------------+--------------+------------------+-----------+------------+----------------------+---------------------------+--------------------+-------------------+------------+------------------------------------+-------------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
workload_group_resource_usage
The WRITE_BUFFER_USAGE_BYTES field has been added, representing the memory usage of Memtables for ingestion tasks within the workload group.
mysql [information_schema]>select * from workload_group_resource_usage;
+-------+-------------------+--------------------+-------------------+-----------------------------+------------------------------+--------------------------+
| BE_ID | WORKLOAD_GROUP_ID | MEMORY_USAGE_BYTES | CPU_USAGE_PERCENT | LOCAL_SCAN_BYTES_PER_SECOND | REMOTE_SCAN_BYTES_PER_SECOND | WRITE_BUFFER_USAGE_BYTES |
+-------+-------------------+--------------------+-------------------+-----------------------------+------------------------------+--------------------------+
| 10009 | 1 | 102314948 | 0.69 | 0 | 0 | 23404836 |
+-------+-------------------+--------------------+-------------------+-----------------------------+------------------------------+--------------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
Testing
Test Environment
Machine Configuration
The test used Alibaba Cloud servers with the following specific configurations:
1FE:
16 cores(vCPU) 32 GiB 200 Mbps ecs.c6.4xlarge
3BE:
16 cores(vCPU) 64 GiB 0 Mbps ecs.g6.4xlarge
测试数据
The test data used TPC-DS 10TB as input, sourced from Alibaba Cloud DLF, and mounted to Doris using the Catalog method. The SQL statement is as follows:
CREATE CATALOG dlf PROPERTIES (
"type"="hms",
"hive.metastore.type" = "dlf",
"dlf.proxy.mode" = "DLF_ONLY",
"dlf.endpoint" = "dlf-vpc.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com",
"dlf.region" = "cn-beijing",
"dlf.uid" = "217316283625971977",
"dlf.catalog.id" = "emr_dev",
"dlf.access_key" = "fill in as applicable",
"dlf.secret_key" = "fill in as applicable"
);
Reference website: https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/docs/dev/benchmark/tpcds
Test Results
The dataset size was 10TB. The ratio of memory to dataset size was 1:52. The overall runtime was 32,000 seconds, and all 99 queries were successfully executed. In the future, we will provide spilling capabilities for more operators (such as window functions, Intersect, etc.) and continue to optimize performance under spilling conditions, reduce disk consumption, and improve query stability.
| query | Time(ms) |
|---|---|
| query1 | 25590 |
| query2 | 126445 |
| query3 | 103859 |
| query4 | 1174702 |
| query5 | 266281 |
| query6 | 62950 |
| query7 | 212745 |
| query8 | 67000 |
| query9 | 602291 |
| query10 | 70904 |
| query11 | 544436 |
| query12 | 25759 |
| query13 | 229144 |
| query14 | 1120895 |
| query15 | 29409 |
| query16 | 117287 |
| query17 | 260122 |
| query18 | 97453 |
| query19 | 127384 |
| query20 | 32749 |
| query21 | 4471 |
| query22 | 10162 |
| query23 | 1772561 |
| query24 | 535506 |
| query25 | 272458 |
| query26 | 83342 |
| query27 | 175264 |
| query28 | 887007 |
| query29 | 427229 |
| query30 | 13661 |
| query31 | 108778 |
| query32 | 37303 |
| query33 | 181351 |
| query34 | 84159 |
| query35 | 81701 |
| query36 | 152990 |
| query37 | 36815 |
| query38 | 172531 |
| query39 | 20155 |
| query40 | 75749 |
| query41 | 527 |
| query42 | 95910 |
| query43 | 66821 |
| query44 | 209947 |
| query45 | 26946 |
| query46 | 131490 |
| query47 | 158011 |
| query48 | 149482 |
| query49 | 303515 |
| query50 | 298089 |
| query51 | 156487 |
| query52 | 97440 |
| query53 | 98258 |
| query54 | 202583 |
| query55 | 93268 |
| query56 | 185255 |
| query57 | 80308 |
| query58 | 252746 |
| query59 | 171545 |
| query60 | 202915 |
| query61 | 272184 |
| query62 | 38749 |
| query63 | 94327 |
| query64 | 247074 |
| query65 | 270705 |
| query66 | 101465 |
| query67 | 3744186 |
| query68 | 151543 |
| query69 | 15559 |
| query70 | 132505 |
| query71 | 180079 |
| query72 | 3085373 |
| query73 | 82623 |
| query74 | 330087 |
| query75 | 830993 |
| query76 | 188805 |
| query77 | 239730 |
| query78 | 1895765 |
| query79 | 144829 |
| query80 | 463652 |
| query81 | 15319 |
| query82 | 76961 |
| query83 | 32437 |
| query84 | 22849 |
| query85 | 58186 |
| query86 | 33933 |
| query87 | 185421 |
| query88 | 434867 |
| query89 | 108265 |
| query90 | 31131 |
| query91 | 18864 |
| query92 | 24510 |
| query93 | 281904 |
| query94 | 67761 |
| query95 | 3738968 |
| query96 | 47245 |
| query97 | 536702 |
| query98 | 97800 |
| query99 | 62210 |
| sum | 31797707 |

