Performance Testing and Analysis
This document introduces the query and ingestion performance of Doris ANN Index. All benchmarks are conducted using VectorDBBench.
Test Environment
All machines used in the tests have 16 CPU cores and 64 GB memory, with CPUs of model Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8369B CPU @ 2.70GHz. FE and BE are co-located on a single 16C64GB machine (note: this is not a recommended production deployment; in production, FE and BE should be deployed separately). The tested version is Apache Doris 4.0.2. The dataset used is VectorDBBench Performance768D1M, which contains 1 million vectors of 768 dimensions.
Results
Analysis
┌──────────────────────┐
│ Recall │
│ (Higher is Better) │
└──────────▲───────────┘
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
┌───────────┘ └───────────┐
│ │
│ │
▼ ▼
┌──────────────────────┐ ┌────────────────────────┐
│ Query QPS │ │ Indexing Throughput │
│ (Latency / QPS) │ │ (Higher is Better) │
│ (Lower Latency Better)│ │ │
└──────────────────────┘ └────────────────────────┘
In vector search, a production-ready vector database typically faces a performance “triangle” that is hard to maximize across all dimensions simultaneously: query performance (QPS/latency), recall, and indexing throughput. System design often requires trade-offs among these three.
Take HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World), the most widely used vector index, as an example. It relies on graph structures to optimize search. There are three key tunable hyperparameters in HNSW:
- max_degree: The maximum out-degree of each node in the graph, determining graph density and connectivity.
- ef_construction: The candidate set size used during index building. Larger values generally result in higher-quality graphs.
- hnsw_ef_search: The exploration window size during query time, directly affecting recall and latency.
In principle, increasing max_degree and ef_construction during index building can significantly improve graph connectivity and navigability, yielding higher recall. A higher-quality graph also allows a smaller hnsw_ef_search at query time, reducing search cost and improving query performance. However, these index-building parameter increases come with trade-offs: index construction requires more compute and memory resources, leading to lower ingestion performance. This is the quintessential trilemma in vector database design.
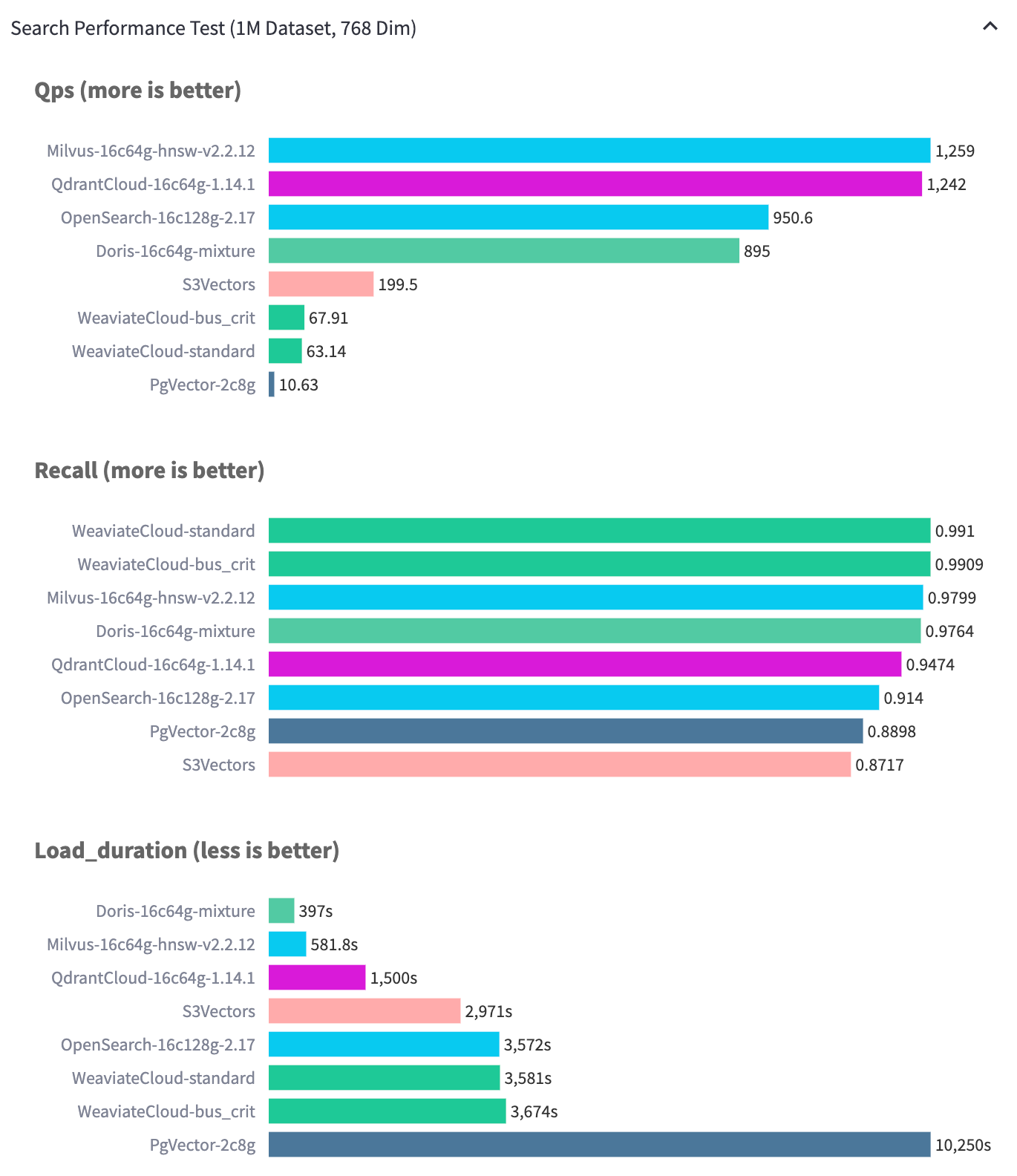
Apache Doris aims to build a more balanced performance triangle for vector search. Through optimizations in the execution engine, storage format improvements, and engineering-level parallel acceleration of HNSW construction, Doris significantly improves overall indexing throughput without sacrificing index quality or high recall.
On the Performance768D1M dataset, results show that, under comparable index quality, Apache Doris exhibits notably better ingestion performance than peer systems. More importantly, Doris does not compromise graph quality to gain ingestion speed. In our tests, Apache Doris achieves a QPS of 989.1 while maintaining over 97% recall, striking a strong balance across all three dimensions of the performance triangle.
Reproduction
NUM_PER_BATCH=500000 vectordbbench doris --host 127.0.0.1 --port 9030 --http-port 8030 --case-type Performance768D1M --db-name vdb --num-concurrency 80 --stream-load-rows-per-batch 500000 --index-prop max_degree=128,ef_construction=256 --session-var hnsw_ef_search=100
