Data Update Overview
In today's data-driven decision-making landscape, data "freshness" has become a core competitive advantage for enterprises to stand out in fierce market competition. Traditional T+1 data processing models, due to their inherent latency, can no longer meet the stringent real-time requirements of modern business. Whether it's achieving millisecond-level synchronization between business databases and data warehouses, dynamically adjusting operational strategies, or correcting erroneous data within seconds to ensure decision accuracy, robust real-time data update capabilities are crucial.
Apache Doris, as a modern real-time analytical database, has one of its core design goals to provide ultimate data freshness. Through its powerful data models and flexible update mechanisms, it successfully compresses data analysis latency from day-level and hour-level to second-level, providing a solid foundation for users to build real-time, agile business decision-making loops.
This document serves as an official guide that systematically explains Apache Doris's data update capabilities, covering its core principles, diverse update and deletion methods, typical application scenarios, and performance best practices under different deployment modes, aiming to help you comprehensively master and efficiently utilize Doris's data update functionality.
1. Core Concepts: Table Models and Update Mechanisms
In Doris, the Data Model of a data table determines its data organization and update behavior. To support different business scenarios, Doris provides three table models: Unique Key Model, Aggregate Key Model, and Duplicate Key Model. Among these, the Unique Key Model is the core for implementing complex, high-frequency data updates.
1.1. Table Model Overview
| Table Model | Key Features | Update Capability | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unique Key Model | Built for real-time updates. Each data row is identified by a unique Primary Key, supporting row-level UPSERT (Update/Insert) and partial column updates. | Strongest, supports all update and deletion methods. | Order status updates, real-time user tag computation, CDC data synchronization, and other scenarios requiring frequent, real-time changes. |
| Aggregate Key Model | Pre-aggregates data based on specified Key columns. For rows with the same Key, Value columns are merged according to defined aggregation functions (such as SUM, MAX, MIN, REPLACE). | Limited, supports REPLACE-style updates and deletions based on Key columns. | Scenarios requiring real-time summary statistics, such as real-time reports, advertisement click statistics, etc. |
| Duplicate Key Model | Data only supports append-only writes, without any deduplication or aggregation operations. Even identical data rows are retained. | Limited, only supports conditional deletion through DELETE statements. | Log collection, user behavior tracking, and other scenarios that only need appending without updates. |
1.2. Data Update Methods
Doris provides two major categories of data update methods: updating through data load and updating through DML statements.
1.2.1. Updating Through Load (UPSERT)
This is Doris's recommended high-performance, high-concurrency update method, primarily targeting the Unique Key Model. All load methods (Stream Load, Broker Load, Routine Load, INSERT INTO) naturally support UPSERT semantics. When new data is loaded, if its primary key already exists, Doris will overwrite the old row data with the new row data; if the primary key doesn't exist, it will insert a new row.
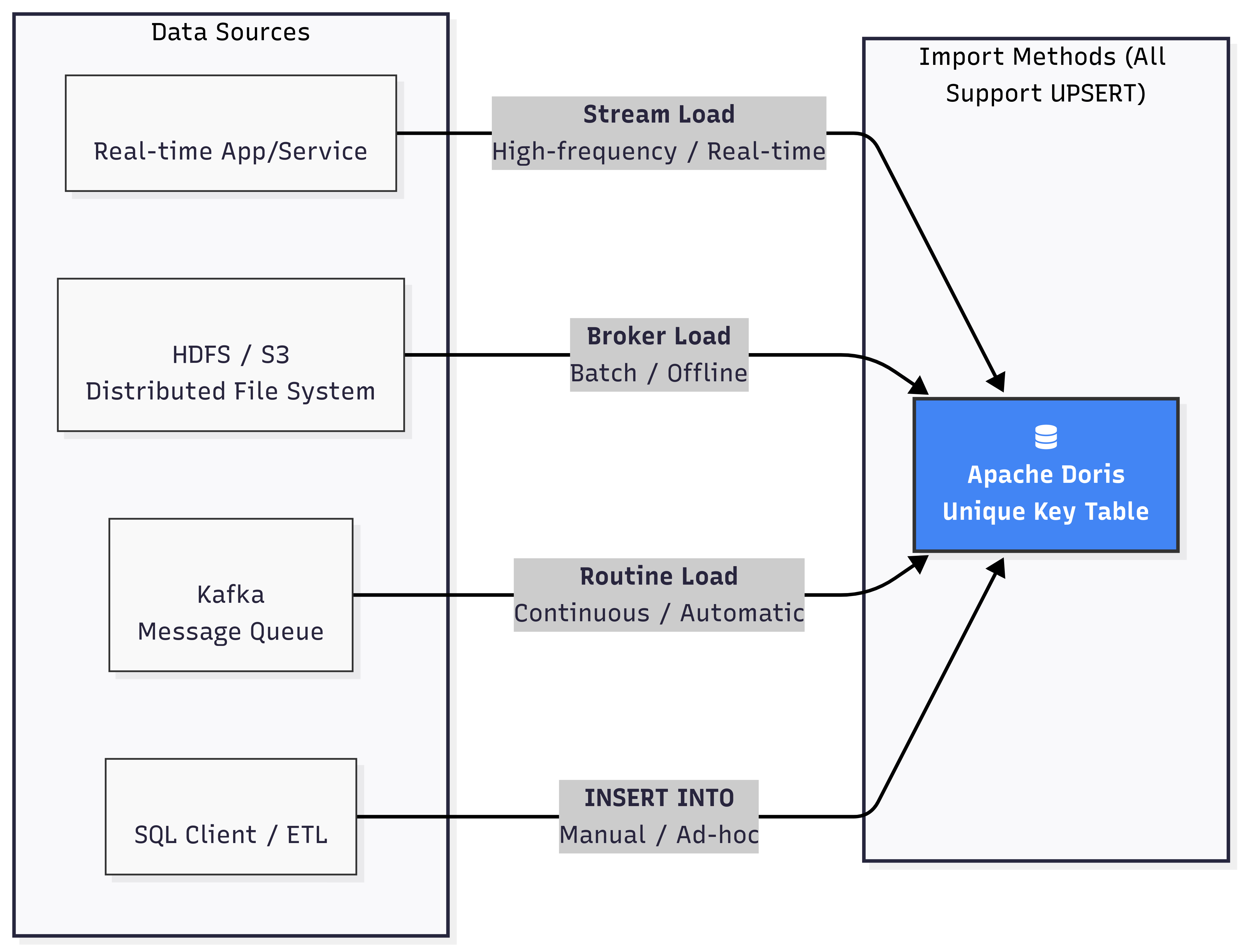
1.2.2. Updating Through UPDATE DML Statements
Doris supports standard SQL UPDATE statements, allowing users to update data based on conditions specified in the WHERE clause. This method is very flexible and supports complex update logic, such as cross-table join updates.
-- Simple update
UPDATE user_profiles SET age = age + 1 WHERE user_id = 1;
-- Cross-table join update
UPDATE sales_records t1
SET t1.user_name = t2.name
FROM user_profiles t2
WHERE t1.user_id = t2.user_id;
Note: The execution process of UPDATE statements involves first scanning data that meets the conditions, then rewriting the updated data back to the table. It's suitable for low-frequency, batch update tasks. High-concurrency operations on UPDATE statements are not recommended because concurrent UPDATE operations involving the same primary keys cannot guarantee data isolation.
1.2.3. Updating Through INSERT INTO SELECT DML Statements
Since Doris provides UPSERT semantics by default, using INSERT INTO SELECT can also achieve similar update effects as UPDATE.
1.3. Data Deletion Methods
Similar to updates, Doris also supports deleting data through both load and DML statements.
1.3.1. Mark Deletion Through Load
This is an efficient batch deletion method, primarily used for the Unique Key Model. Users can add a special hidden column DORIS_DELETE_SIGN when loading data. When the value of this column for a row is 1 or true, Doris will mark the corresponding data row with that primary key as deleted (the principle of delete sign will be explained in detail later).
// Stream Load load data, delete row with user_id = 2
// curl --location-trusted -u user:passwd -H "columns:user_id, __DORIS_DELETE_SIGN__" -T delete.json http://fe_host:8030/api/db_name/table_name/_stream_load
// delete.json content
[
{"user_id": 2, "__DORIS_DELETE_SIGN__": "1"}
]
1.3.2. Deletion Through DELETE DML Statements
Doris supports standard SQL DELETE statements that can delete data based on WHERE conditions.
- Unique Key Model:
DELETEstatements will rewrite the primary keys of rows meeting the conditions with deletion marks. Therefore, its performance is proportional to the amount of data to be deleted. The execution principle ofDELETEstatements on Unique Key Models is very similar toUPDATEstatements, first reading the data to be deleted through queries, then writing it once more with deletion marks. Compared toUPDATEstatements, DELETE statements only need to write Key columns and deletion mark columns, making them relatively lighter. - Duplicate/Aggregate Models:
DELETEstatements are implemented by recording a delete predicate. During queries, this predicate serves as a runtime filter to filter out deleted data. Therefore,DELETEoperations themselves are very fast, almost independent of the amount of deleted data. However, note that high-frequencyDELETEoperations on Duplicate/Aggregate Models will accumulate many runtime filters, severely affecting subsequent query performance.
DELETE FROM user_profiles WHERE last_login < '2022-01-01';
The following table provides a brief summary of using DML statements for deletion:
| Unique Key Model | Aggregate Model | Duplicate Model | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation | Delete Sign | Delete Predicate | Delete Predicate |
| Limitations | None | Delete conditions only for Key columns | None |
| Deletion Performance | Moderate | Fast | Fast |
2. Deep Dive into Unique Key Model: Principles and Implementation
The Unique Key Model is the cornerstone of Doris's high-performance real-time updates. Understanding its internal working principles is crucial for fully leveraging its performance.
2.1. Merge-on-Write (MoW) vs. Merge-on-Read (MoR)
The Unique Key Model has two data merging strategies: Merge-on-Write (MoW) and Merge-on-Read (MoR). Since Doris 2.1, MoW has become the default and recommended implementation.
| Feature | Merge-on-Write (MoW) | Merge-on-Read (MoR) - (Legacy) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Concept | Completes data deduplication and merging during data writing, ensuring only one latest record per primary key in storage. | Retains multiple versions during data writing, performs real-time merging during queries to return the latest version. |
| Query Performance | Extremely high. No additional merge operations needed during queries, performance approaches that of non-updated detail tables. | Poor. Requires data merging during queries, taking about 3-10 times longer than MoW and consuming more CPU and memory. |
| Write Performance | Has merge overhead during writing, with some performance loss compared to MoR (about 10-20% for small batches, 30-50% for large batches). | Fast writing speed, approaching detail tables. |
| Resource Consumption | Consumes more CPU and memory during writing and background Compaction. | Consumes more CPU and memory during queries. |
| Use Cases | Most real-time update scenarios. Especially suitable for read-heavy, write-light businesses, providing ultimate query analysis performance. | Suitable for write-heavy, read-light scenarios, but no longer mainstream recommended. |
The MoW mechanism trades a small cost during the writing phase for tremendous improvement in query performance, perfectly aligning with the OLAP system's "read-heavy, write-light" characteristics.
2.2. Conditional Updates (Sequence Column)
In distributed systems, out-of-order data arrival is a common problem. For example, an order status changes sequentially to "Paid" and "Shipped", but due to network delays, data representing "Shipped" might arrive at Doris before data representing "Paid".
To solve this problem, Doris introduces the Sequence Column mechanism. Users can specify a column (usually a timestamp or version number) as the Sequence column when creating tables. When processing data with the same primary key, Doris will compare their Sequence column values and always retain the row with the largest Sequence value, thus ensuring eventual consistency even when data arrives out of order.
CREATE TABLE order_status (
order_id BIGINT,
status_name STRING,
update_time DATETIME
)
UNIQUE KEY(order_id)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(order_id)
PROPERTIES (
"function_column.sequence_col" = "update_time" -- Specify update_time as Sequence column
);
-- 1. Write "Shipped" record (larger update_time)
-- {"order_id": 1001, "status_name": "Shipped", "update_time": "2023-10-26 12:00:00"}
-- 2. Write "Paid" record (smaller update_time, arrives later)
-- {"order_id": 1001, "status_name": "Paid", "update_time": "2023-10-26 11:00:00"}
-- Final query result, retains record with largest update_time
-- order_id: 1001, status_name: "Shipped", update_time: "2023-10-26 12:00:00"
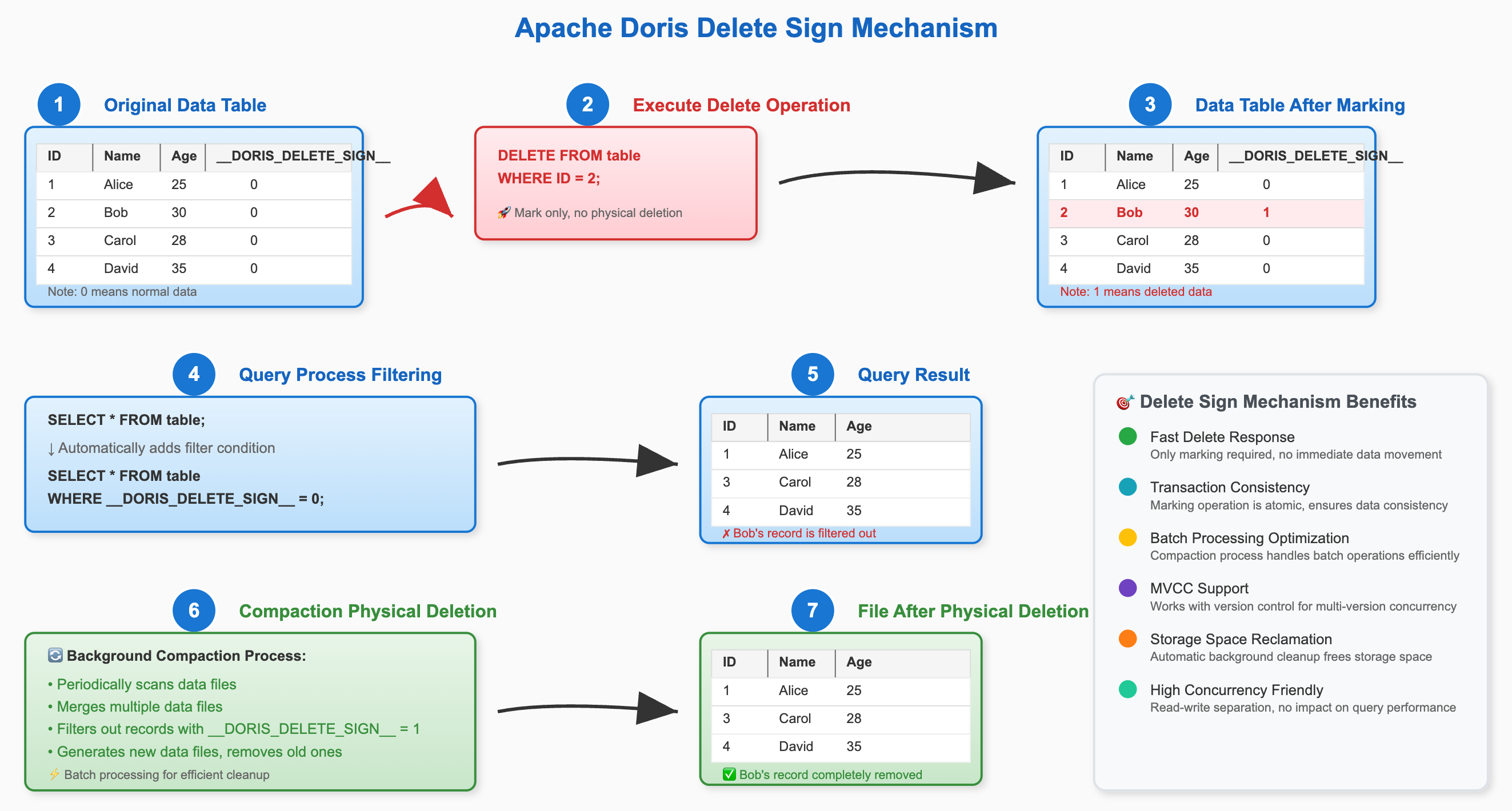
2.3. Deletion Mechanism (DORIS_DELETE_SIGN) Workflow
The working principle of DORIS_DELETE_SIGN can be summarized as "logical marking, background cleanup".
- Execute Deletion: When users delete data through load or
DELETEstatements, Doris doesn't immediately remove data from physical files. Instead, it writes a new record for the primary key to be deleted, with theDORIS_DELETE_SIGNcolumn marked as1. - Query Filtering: When users query data, Doris automatically adds a filter condition
WHERE DORIS_DELETE_SIGN = 0to the query plan, thus hiding all data marked for deletion from query results. - Background Compaction: Doris's background Compaction process periodically scans data. When it finds a primary key with both normal records and deletion mark records, it will physically remove both records during the merge process, eventually freeing storage space.
This mechanism ensures quick response to deletion operations while asynchronously completing physical cleanup through background tasks, avoiding performance impact on online business.
The following diagram shows how DORIS_DELETE_SIGN works:
2.4 Partial Column Update
Starting from version 2.0, Doris supports powerful partial column update capabilities on Unique Key Models (MoW). When loading data, users only need to provide the primary key and columns to be updated; unprovided columns will maintain their original values unchanged. This greatly simplifies ETL processes for scenarios like wide table joining and real-time tag updates.
To enable this feature, you need to enable Merge-on-Write (MoW) mode when creating the Unique Key Model table. For INSERT INTO, set the session variable enable_unique_key_partial_update to true to enable partial column updates; for Stream Load and other import methods, configure the partial_columns parameter to enable partial column updates.
CREATE TABLE user_profiles (
user_id BIGINT,
name STRING,
age INT,
last_login DATETIME
)
UNIQUE KEY(user_id)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(user_id)
PROPERTIES (
"enable_unique_key_merge_on_write" = "true"
);
-- Initial data
-- user_id: 1, name: 'Alice', age: 30, last_login: '2023-10-01 10:00:00'
-- load partial update data through Stream Load, only updating age and last_login
-- {"user_id": 1, "age": 31, "last_login": "2023-10-26 18:00:00"}
-- Updated data
-- user_id: 1, name: 'Alice', age: 31, last_login: '2023-10-26 18:00:00'
Partial Column Update Principle Overview
Unlike traditional OLTP databases, Doris's partial column update is not in-place data update. To achieve better write throughput and query performance in Doris, partial column updates in Unique Key Models adopt an "load-time missing field completion followed by full-row writing" implementation approach.
Therefore, using Doris's partial column update has "read amplification" and "write amplification" effects. For example, updating 10 fields in a 100-column wide table requires Doris to complete the missing 90 fields during the write process. Assuming each field has similar size, a 1MB 10-field update will generate approximately 9MB of data reading (completing missing fields) and 10MB of data writing (writing the complete row to new files) in the Doris system, resulting in about 9x read amplification and 10x write amplification.
Partial Column Update Performance Recommendations
Due to read and write amplification in partial column updates, and since Doris is a columnar storage system, the data reading process may generate significant random I/O, requiring high random read IOPS from storage. Since traditional mechanical disks have significant bottlenecks in random I/O, if you want to use partial column update functionality for high-frequency writes, SSD drives are recommended, preferably NVMe interface, which can provide the best random I/O support.
Additionally, if the table is very wide, enabling row storage is also recommended to reduce random I/O. After enabling row storage, Doris will store an additional copy of row-based data alongside columnar storage. Since row-based data stores each row continuously, it can read entire rows with a single I/O operation (columnar storage requires N I/O operations to read all missing fields, such as the previous example of a 100-column wide table updating 10 columns, requiring 90 I/O operations per row to read all fields).
3. Typical Application Scenarios
Doris's powerful data update capabilities enable it to handle various demanding real-time analysis scenarios.
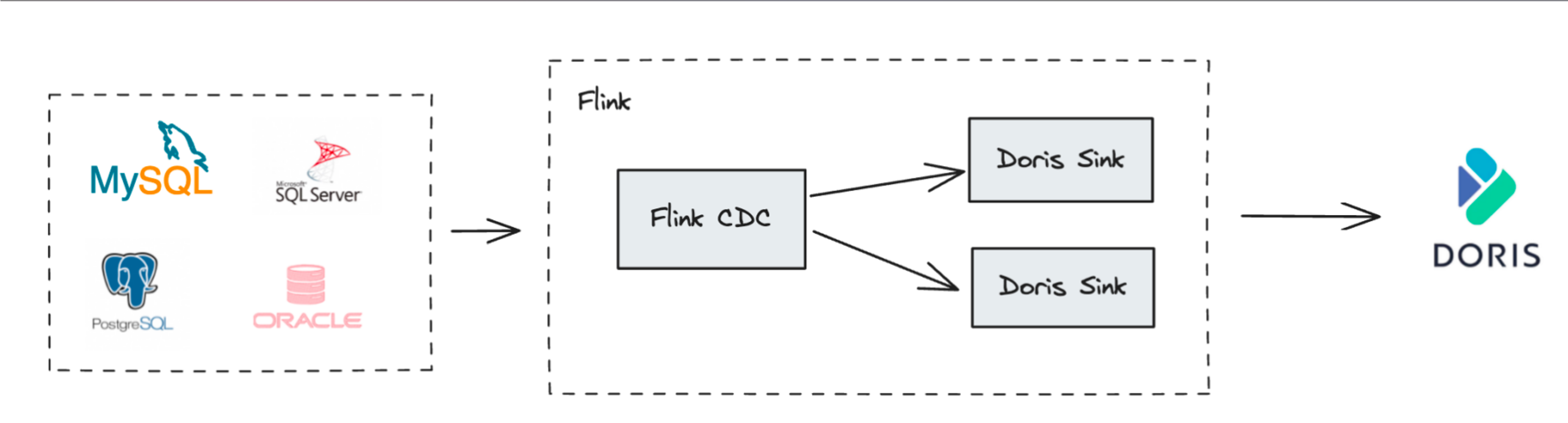
3.1. CDC Real-time Data Synchronization
Capturing change data (Binlog) from upstream business databases (such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle) through tools like Flink CDC and writing it in real-time to Doris Unique Key Model tables is the most classic scenario for building real-time data warehouses.
- Whole Database Synchronization: Flink Doris Connector internally integrates Flink CDC, enabling automated, end-to-end whole database synchronization from upstream databases to Doris without manual table creation and field mapping configuration.
- Ensuring Consistency: Utilizes the Unique Key Model's
UPSERTcapability to handle upstreamINSERTandUPDATEoperations, usesDORIS_DELETE_SIGNto handleDELETEoperations, and combines with Sequence columns (such as timestamps in Binlog) to handle out-of-order data, perfectly replicating upstream database states and achieving millisecond-level data synchronization latency.
3.2. Real-time Wide Table Joining
In many analytical scenarios, data from different business systems needs to be joined into user-wide tables or product-wide tables. Traditional approaches use offline ETL tasks (such as Spark or Hive) for periodic (T+1) joining, which has poor real-time performance and high maintenance costs. Alternatively, using Flink for real-time wide table join calculations and writing joined data to databases typically requires significant computational resources.
Using Doris's partial column update capability can greatly simplify this process:
- Create a Unique Key Model wide table in Doris.
- Write data streams from different sources (such as user basic information, user behavior data, transaction data, etc.) to this wide table in real-time through Stream Load or Routine Load.
- Each data stream only updates its relevant fields. For example, user behavior data streams only update
page_view_count,last_login_time, and other fields; transaction data streams only updatetotal_orders,total_amount, and other fields.
This approach not only transforms wide table construction from offline ETL to real-time stream processing, greatly improving data freshness, but also reduces I/O overhead by only writing changed columns, improving write performance.
4. Best Practices
Following these best practices can help you use Doris's data update functionality more stably and efficiently.
4.1. General Performance Practices
- Prioritize load Updates: For high-frequency, large-volume update operations, prioritize load methods like Stream Load and Routine Load over
UPDATEDML statements. - Batch Writes: Avoid using
INSERT INTOstatements for individual high-frequency writes (such as > 100 TPS), as eachINSERTincurs transaction overhead. If necessary, consider enabling Group Commit functionality to merge multiple small batch commits into one large transaction. - Use High-frequency
DELETECarefully: On Duplicate and Aggregate models, avoid high-frequencyDELETEoperations to prevent query performance degradation. - Use
TRUNCATE PARTITIONfor Partition Data Deletion: If you need to delete entire partition data, useTRUNCATE PARTITION, which is much more efficient thanDELETE. - Execute
UPDATESerially: Avoid concurrent execution ofUPDATEtasks that might affect the same data rows.
4.2. Unique Key Model Practices in Compute-Storage Separation Architecture
Doris 3.0 introduces an advanced compute-storage separation architecture, bringing ultimate elasticity and lower costs. In this architecture, since BE nodes are stateless, a global state needs to be maintained through MetaService during the Merge-on-Write process to resolve write-write conflicts between load/compaction/schema change operations. The MoW implementation of Unique Key Models relies on a distributed table lock based on Meta Service to ensure write operation consistency, as shown in the following diagram:
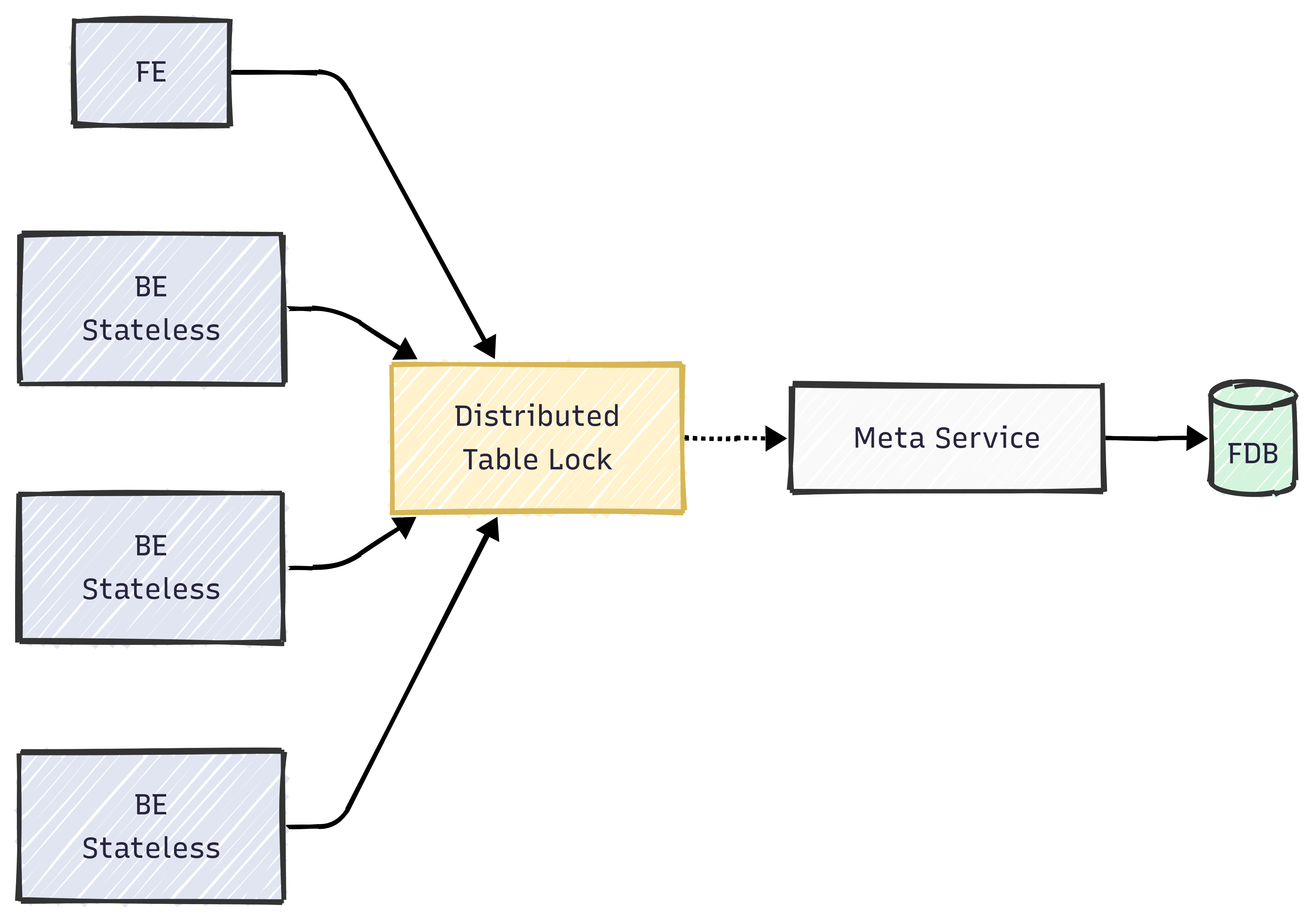
High-frequency loads and Compaction lead to frequent competition for table locks, so special attention should be paid to the following points:
- Control Single Table load Frequency: It's recommended to control the load frequency of a single Unique Key table to within 60 times/second. This can be achieved by batching and adjusting load concurrency.
- Reasonable Partition and Bucket Design:
- Partitions: Using time partitioning (such as by day or hour) ensures that single loads only update a few partitions, reducing the scope of lock competition.
- Buckets: The number of buckets (Tablet count) should be reasonably set based on data volume, typically between 8-64. Too many Tablets will intensify lock competition.
- Adjust Compaction Strategy: In scenarios with very high write pressure, Compaction strategies can be appropriately adjusted to reduce Compaction frequency, thereby reducing lock conflicts between Compaction and load tasks.
- Upgrade to Latest Version: The Doris community is continuously optimizing Unique Key Model performance under compute-storage separation architecture. For example, the upcoming 3.1 release significantly optimizes the distributed table lock implementation. Always recommend using the latest stable version for optimal performance.
Conclusion
Apache Doris, with its powerful, flexible, and efficient data update capabilities centered on the Unique Key Model, truly breaks through the bottleneck of traditional OLAP systems in terms of data freshness. Whether through high-performance loads implementing UPSERT and partial column updates, or using Sequence columns to ensure consistency of out-of-order data, Doris provides complete solutions for building end-to-end real-time analytical applications.
By deeply understanding its core principles, mastering the applicable scenarios for different update methods, and following the best practices provided in this document, you will be able to fully unleash Doris's potential, making real-time data truly become a powerful engine driving business growth.

