A glimpse of the next-generation analytical database
Hello everyone, welcome to the Doris Summit 2022, the first summit of Apache Doris since it was open-sourced. In this lecture, you will go through the development of Doris in 2022 and look into the new trends that Doris is exploring in 2023. My name is Mingyu Chen and I am the PMC Chair of the Apache Doris. I have been developing for Doris since 2014, and witnessed its whole process from open-source to graduation from Apache. My sharing will cover the following aspects. Let's get started.
As the beginning, I will briefly introduce what Doris is and why we should choose Doris in case you are new to Apache Doris. In 2022, Doris has became one of the most active open-sourced big data analysis engine projects in the world while the Doris community became one of the most active open-source communities in China, which you may get interested in. Moreover, the cutting-edge features, such as vectorized execution engine, cloud-native and efficient semi-structured data analysis, real-time processing and Lakehouse will be the focus of my lecture today. Also, it is important to prioritize tasks at the beginning of the year, so I will go through our job list with you shortly.
About Doris
Briefly speaking, Apache Doris is an easy-to-use, high-performance and unified analytical database. As shown in this enterprise data flow chart, you may have a clear vision of where Apache Doris stands. Data from various upstream data sources, such as transactional databases, log systems, event tracking, etc., as well as data from ETL components, such as Flink, Spark and Hive is ingested into Doris through data processing and integration tools.
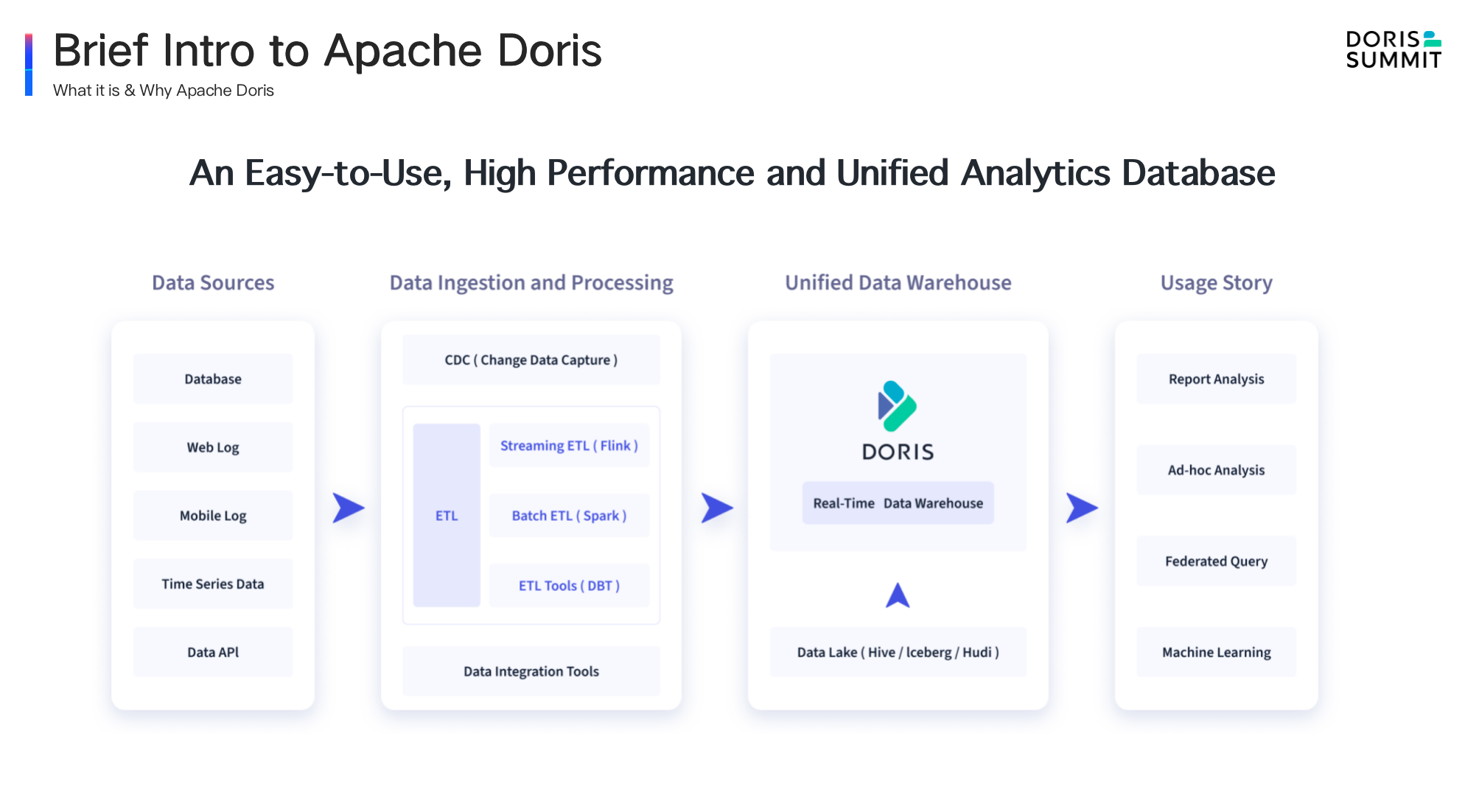
As a fully-complete database system, Doris can provide various direct query functions including report analysis, multi-dimensional analysis, log analysis, user portrait and lakehouse, etc. Thanks to Doris' MPP SQL distributed query engine. Doris can also be used to query external data sources from Hive, Iceberg, Hudi, Elasticsearch and various transactional database systems connected through JDBC, without data import and maintaining the schema of other data sources. There are several core features that can help users solve practical problems, which are as follows:
- NO.1 is the ease of use. It supports ANSI SQL syntax, including single table aggregation, sorting, filtering and multi table join, sub query, etc. It also supports complex SQL syntax such as window function and grouping sets. At the same time, users can expand system functions through UDF, UDAF. In addition, Apache Doris is also compatible with MySQL protocol, which allows users access Doris through various BI tools.
- NO.2 is high performance. Doris is equipped with an efficient column storage engine, which not only reduces the amount of data scanning, but also implements an ultra-high data compression ratio. At the same time, Doris also uses various index technology to speed up data reading and filtering. Using the partition and bucket pruning function, Doris can support ultra-high concurrency of online service business, and a single node can support up to thousands of QPS. Further, Apache Doris combines the vectorized execution engine to give full play to the modern CPU parallel computing power. Doris supports materialized view. In terms of the optimizer, Doris uses a combination of CBO and RBO, with RBO supporting constant folding, subquery rewriting, predicate pushdown, etc.
- NO.3 is unified data warehouse. Thanks to the well-designed architecture, Doris can easily handle both low-latency, high-concurrency scenarios and high-throughput scenarios .
- NO.4 is the federated query analysis. With the help of Doris's complete distributed query engine, Doris can access data lake such as Hive, Iceberg and Hudi, as well as high-speed queries to external data sources such as Elasticsearch and MySQL.
- NO.5 is ecological enrichment. Doris provides rich data ingest methods, supports fast loading of data from localhost, Hadoop, Flink, Spark, Kafka, SeaTunnel and other systems, and can also directly access data in MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, S3, Hive, Iceberg, Elasticsearch and other systems without data replication. At the same time, the data stored in Doris can also be read by Spark and Flink, and can be output to the upstream data application for display and analysis.
Next, we will review what remarkable achievements the Doris community has achieved in 2022.
How should we look back on 2022?
In 2022, the world has witnessed unprecedented changes, and countless magical moments are happening in reality. Thankfully, the power of technology and open source has navigated us to the right path. And 2022 is absolutely a fruitful year for Apache Doris. Let's review the development of Apache Doris in the past year from several angles:
Important Indicators of the Community
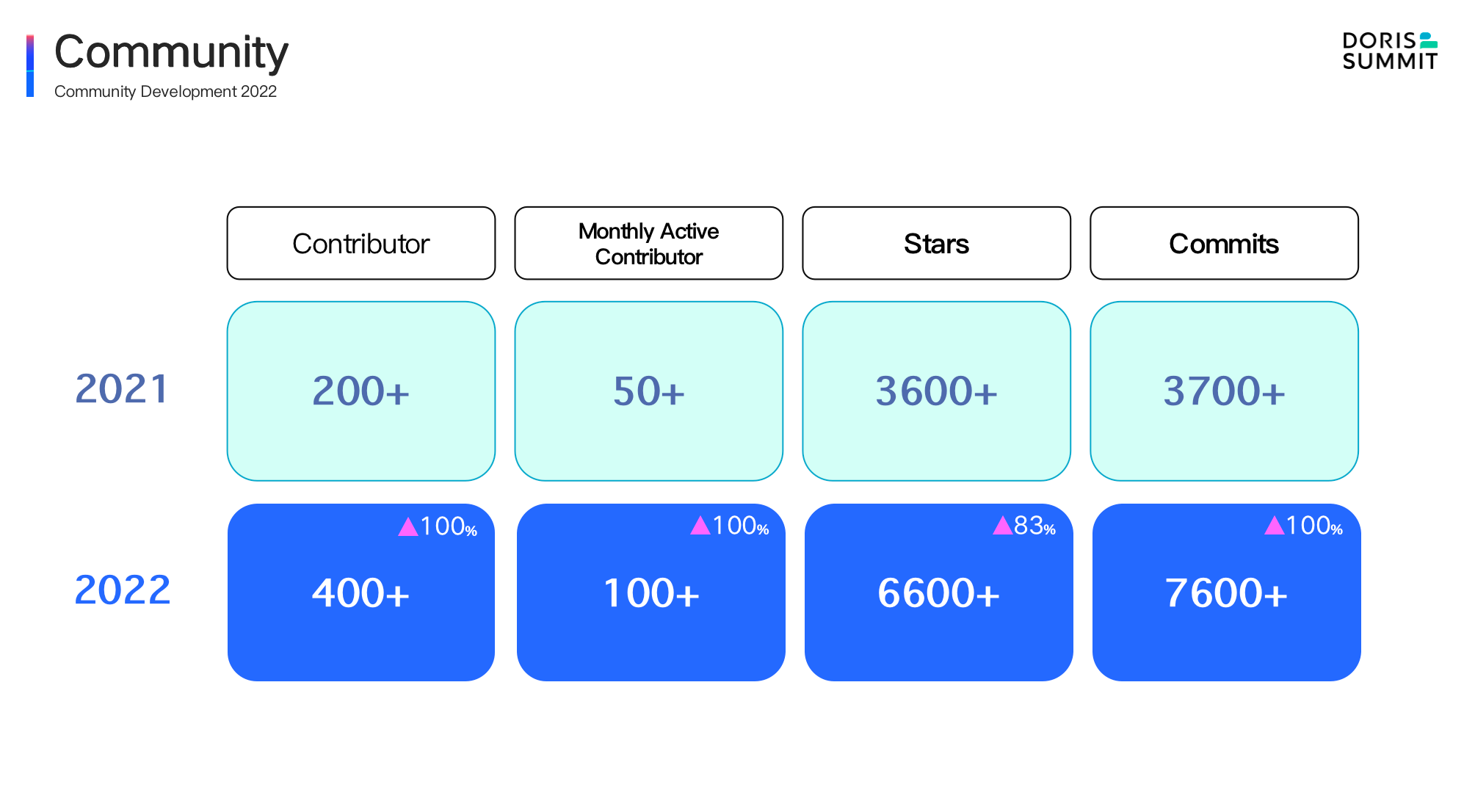
In the past year:
- The number of cumulative community contributors has increased from 200 to nearly 420, a year-on-year increase of more than 100%, which is still rising.
- The number of monthly active contributors has doubled from 50 to 100.
- The number of GitHub Stars has increased from 3.6k to 6.8k, and has been on the daily/weekly/monthly GitHub Trending list many times.
- The number of all Commits increased from 3.7k to 7.6k. The amount of newly submitted code in the past year exceeded the total of previous years.
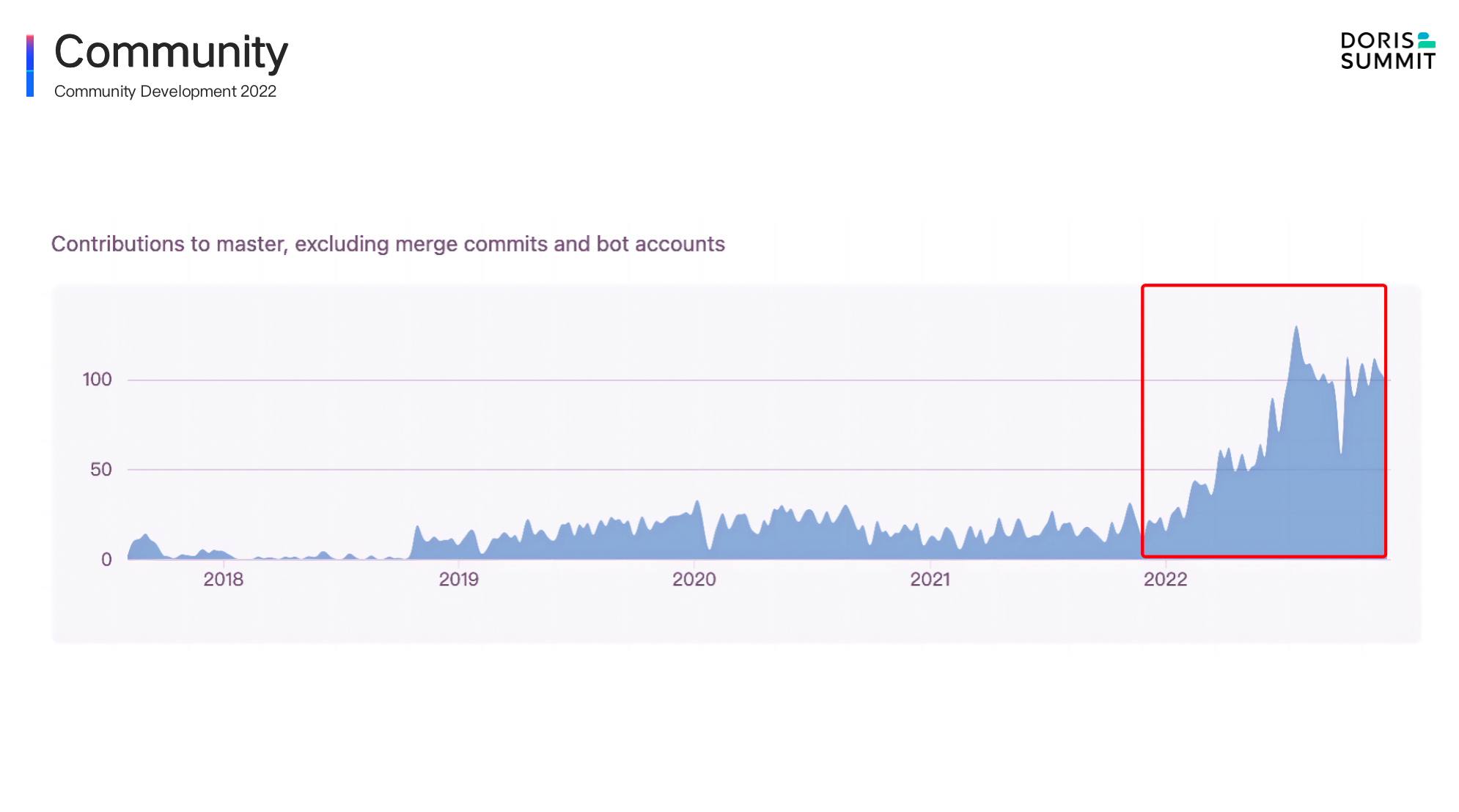
From these data, we can see that in 2022, there was an explosive growth in Apache Doris. The data indicators of all dimensions are grown by nearly 100%. The great effort has also made Apache Doris one of the most active open-source communities in the big data and database world. As is the growth shown in the trending of GitHub Contribution above, users and developers have made tremendous contribution to the community . It is memorable that in June 2022, Apache Doris graduated from the Apache incubator and became a Top-Level Project, which is the biggest milestone since open-souced.
Open Source User Scale
Thanks to the voluntary technical support from the developers of SelectDB, a commercial company with products based on Apache Doris. In 2022 Doris became smoother in user connection and communication, and we were able to interact with users more directly and listen to their real voices. Last year, Apache Doris was applied in dozens of industries, such as the Internet, fintech, telecommunications, education, automobiles, manufacturing, logistics, energy, and government affairs, and especially in the Internet industry, which is known for massive data. 80% of the TOP 50 Chinese Internet companies have been using Apache Doris for a long time to solve data analysis problems in their own business, including Baidu, Meituan, Xiaomi, Tencent, JD.com, ByteDance , NetEase, Sina, 360 Total Security, MiHoYo, ZHIHU.COM, etc.

Globally, Apache Doris has served thousands of enterprise users, and this number is still growing rapidly. Most enterprise users are glad to contact the community and participate in community building through various means. Moreover, many of the enterprise users participated in Doris Summit, giving a lecture of their own practical experience based on real business.
Releases
In the early versions, ease of use has been frequently emphasized. The versions released in 2022 mainly focus on performance, stability, ease of use, which is a comprehensive evolution.
- In April, the community released Apache Doris V1.0.0, whose major version first changed from 0 to 1(V0.1.5 to V1.0.0) since open-sourced. In version 1.0, the extraordinary vectorized execution engine was first published, marking the beginning of Apache Doris to the era of ultra-high speed data analysis.
- In version 1.1 released in June, we further improved and optimized the vectorized engine, and set it as default. Simultaneously, the community has also prepared LTS(Long-Term-Support) versions released to quickly fix bugs and optimize functions for version 1.1 on a monthly basis, aiming to ensure higher stability required by the growing community users.
- Launched in early December, Version 1.2 not only introduces many important functions, such as Merge-on-Write for Unique Key model, Multi-Catalog, Java UDF, Array type, JSONB type, etc., but also improves the query performance by nearly ten times. These features allow Apache Doris to be more adaptable and possible for more data analysis.
- In version 1.2, stability and quality assurance were strongly stressed. On the one hand, using automated testing tools such as SQL Smith and test cases from various well-known open source projects, we have built millions of test case sets; On the other hand, the community access pipeline and perfect regression testing framework ensure the quality of code-merge.
Evolution of Core Features
In 2022, the community's research and development was mainly focused on four aspects, high performance, real-time processing, semi-structured data support and Lakehouse.

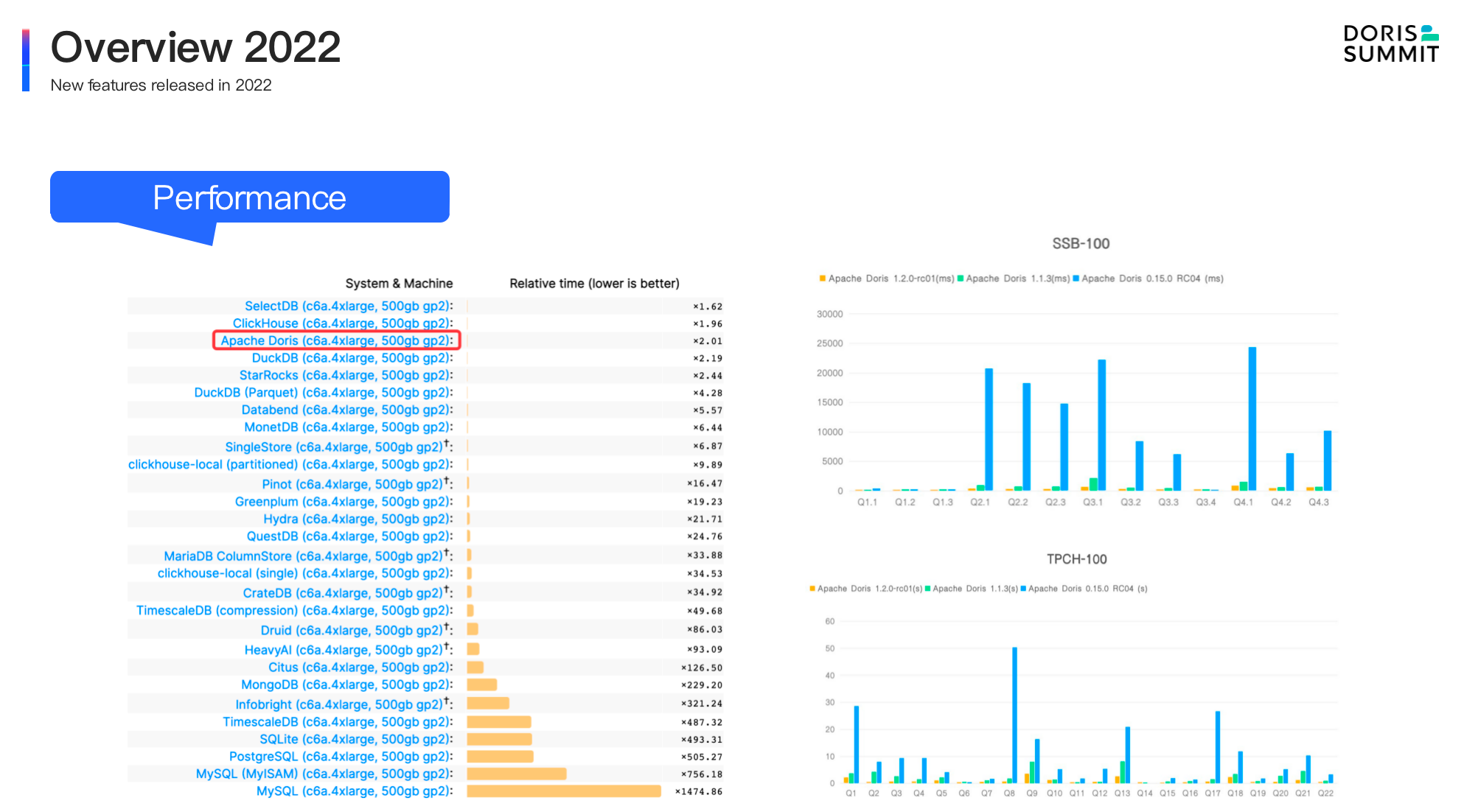
- Query performance improvement. From the released version 1.0 to 1.2, Apache Doris has made remarkable achievement in performance. In the single-table test, Apache Doris won 3rd place in Clickbench database performance list launched by Clickhouse. In the multi-table association, thanks to the vectorized execution engine and various query optimization, compared to the released version 0.15 at the end of 2021, Apache Doris was 10 times faster in standard test data sets under SSB and TPC-H, which marks Apache Doris one of the best databases in the world!
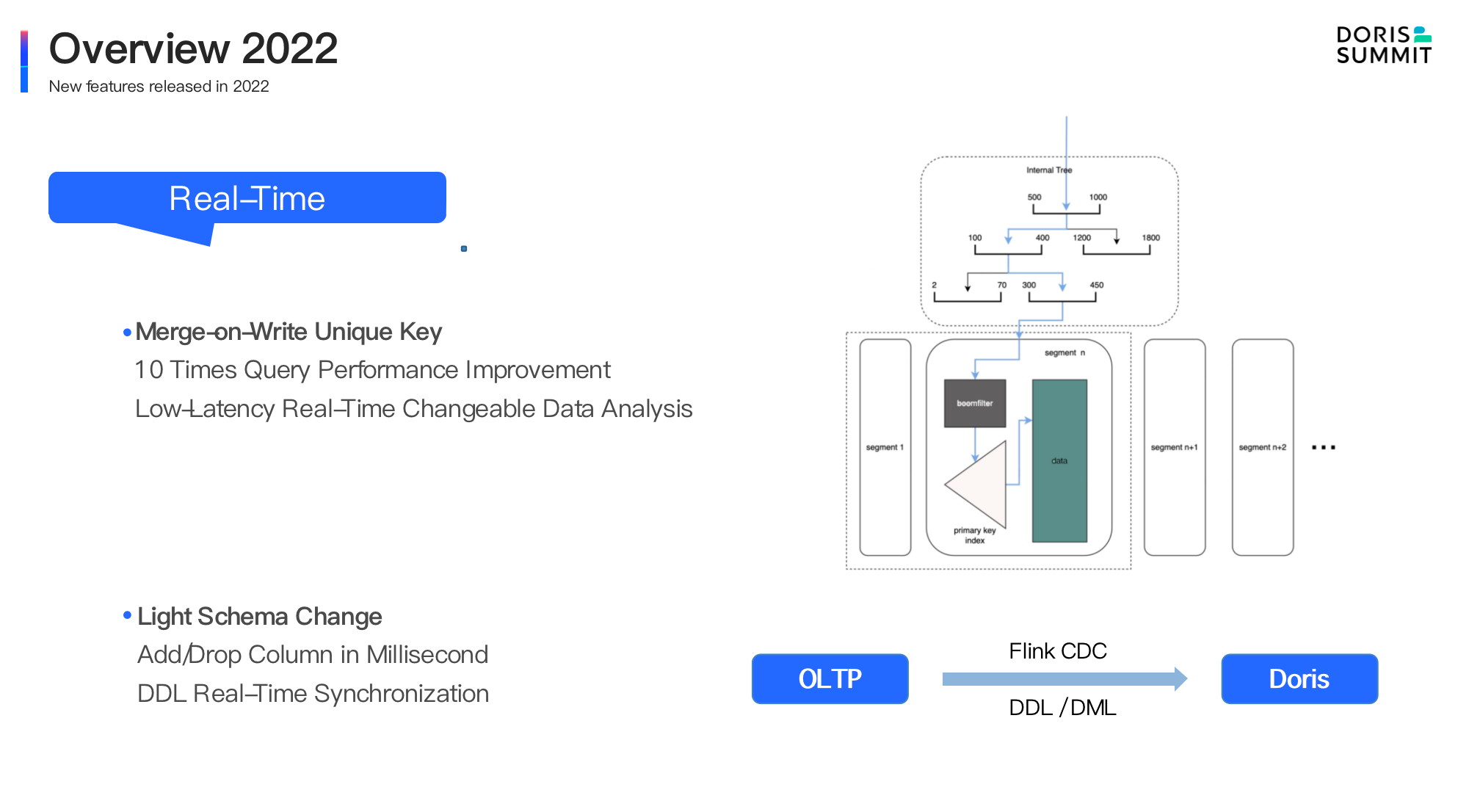
- Real-time processing optimization. In version 1.2, we have implemented the Merge-On-Write data update method on the original Unique Key, with a query performance improved by 5-10 times during high-frequency updates and low latency on updateable data in real-time analytics. In addition, the lightweight Schema Change enables easier column adding and substraction of data, which is unecessary for users to convert historical data any more. Tools such as Flink CDC can be used instantly to synchronize DML or DDL operations in transaction databases, making data synchronization smoother and unified.
- Semi-structured data analysis. At present, Apache Doris supports Array and JSONB types. The Array type can not only store complex data structures, but also support user behavior analysis through Array functions. JSONB is a binary JSON storage type, which not only has 4 times faster access performance than Text JSON, but has lower memory consumption as well. Various log data structures in JSON format can be easily ingested through JSONB efficiently.

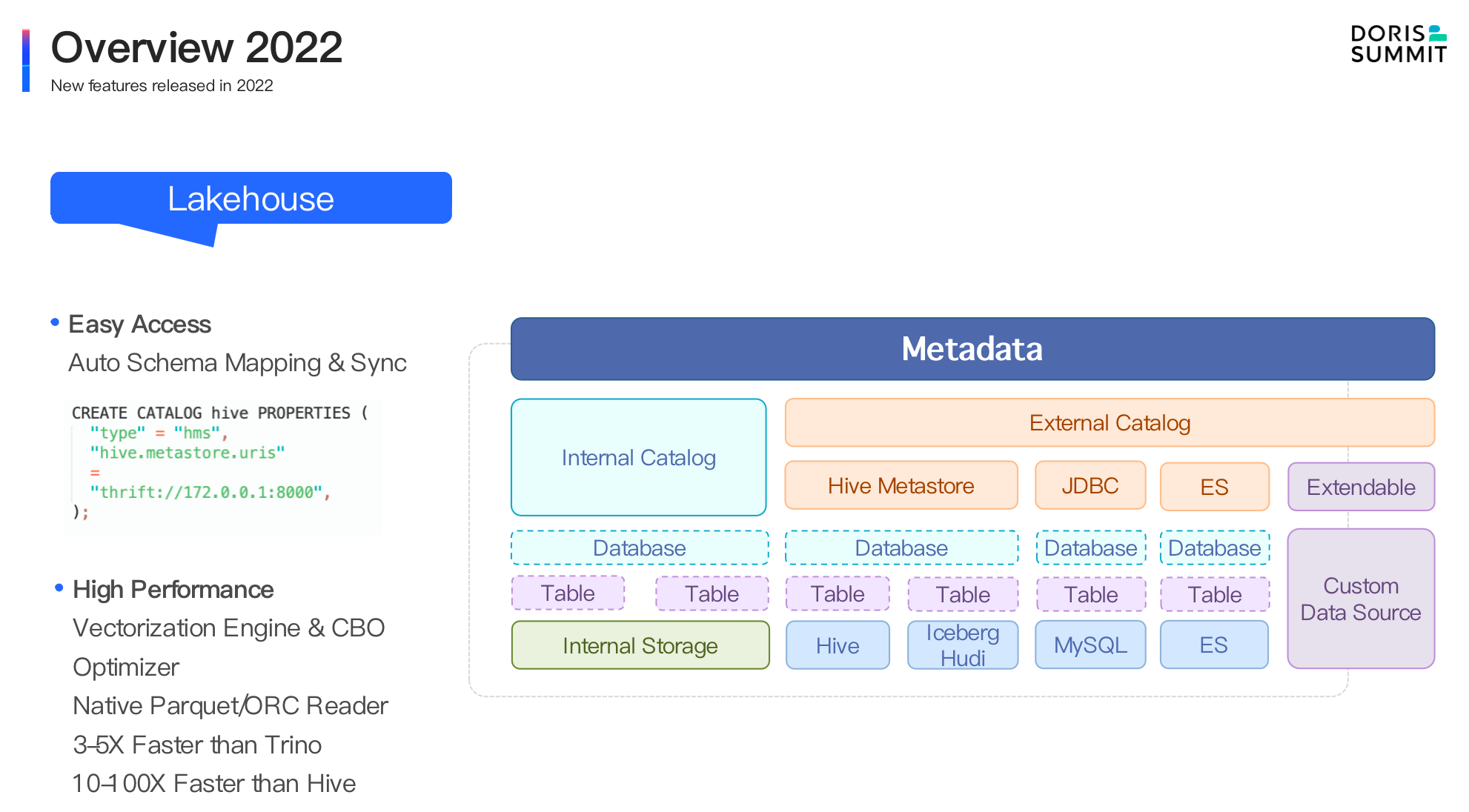
- Lakehouse. In version 1.2.0, through multiple performance optimizations for external data sources such as Native Format Reader, late materialization, asynchronous IO, data prefetching, high-performance execution engine and query optimizer, Apache Doris can easily access external data sources, for instance, Hive, Iceberg and Hudi. And the speed of access is 3-5 times faster than Trino/Presto and 10-100 times faster than Hive.
2023 RoadMap
In 2023, the Apache Doris community will deep dive into new features development, as you can refer to the 2023 RoadMap and the specific plan for next year below:
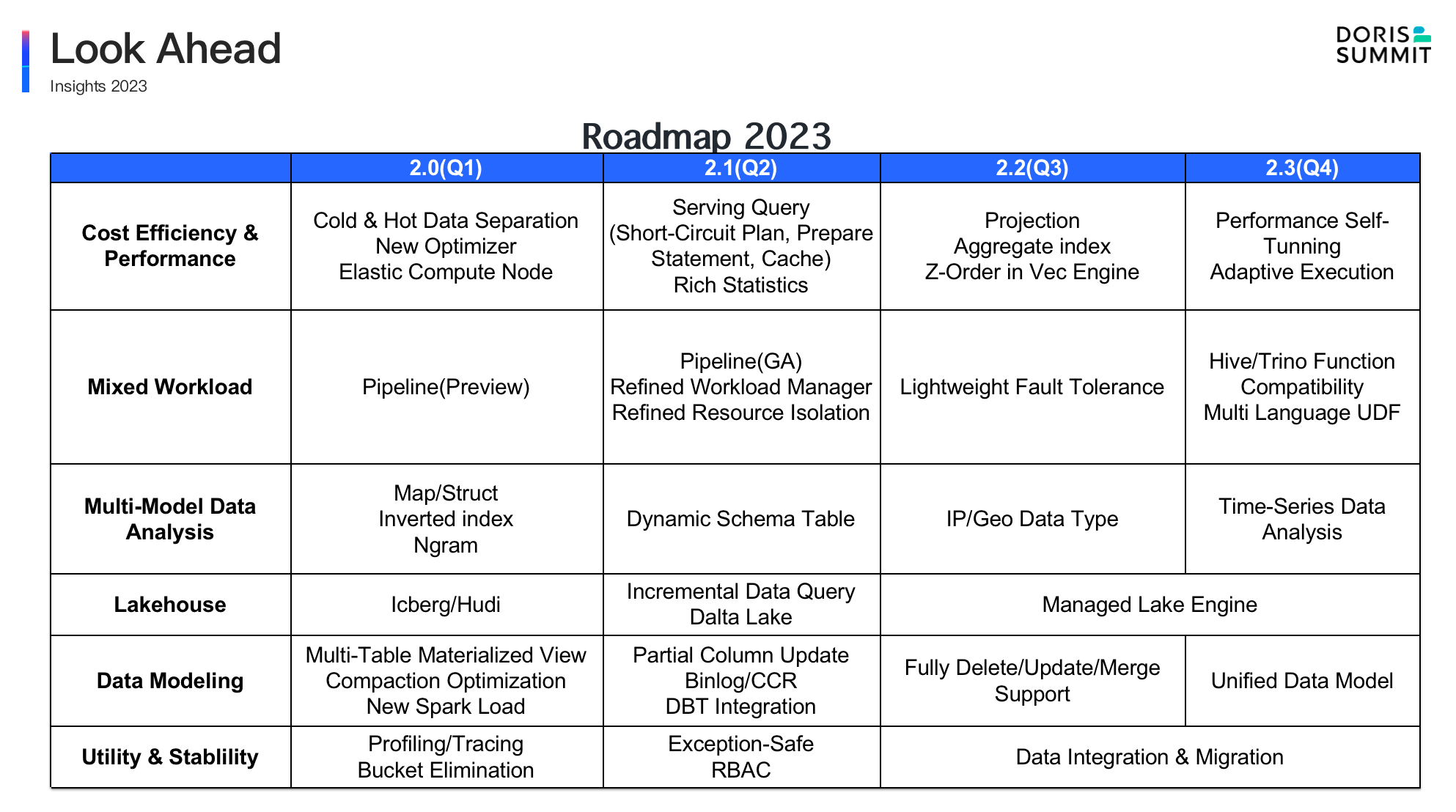
In 2023, we will start the iteration of Apache Doris 2.x version on a quarterly basis . At the same time, for each 2-bit version, bug fixes and upgrades will be done on a monthly basis. From a functional point of view, the follow-up research and development will focus on the following main directions:
High Performance
High performance is the goal that Apache Doris is constantly pursuing. Doris' excellent performance on public test datasets such as Clickbench and TPC-H has proved that it has become industry-leading. In the future, we will further enhance performance, including:
- More complex SQL: The new query optimizer will be available in the first quarter of 2023. The new query optimizer supports the strategy of combining RBO and CBO, and it can support complex queries more efficiently and fully execute all 99 SQLs of TPC-DS.
- Higher concurrency point query: High concurrency is always what Apache Doris is good at. And in 2023 we will further strengthen this capability through a series of features such as Short-Circuit Plan, Prepare Statement, Query Cache, etc., to support ultra-high concurrency of 10,000 QPS with single node and has higher-concurrency scaling out.
- More flexible multi-table materialized views: In previous versions, Apache Doris accelerated the analysis efficiency of fixed-dimensional data through strengthen single-table materialized views. The new multi-table materialized view will decouple the lifecycle of Base table and the MV table. In this way, Doris can easily deal with the multi-table JOINs and the pre-calculation acceleration of more complex SQL queries. And Doris is capable of asynchronous refresh and flexible incremental calculation methods. This feature will be available in the first quarter of 2023.
Cost-effective
Cost efficiency is the key to winning market competition for enterprises, which is true for databases as well. In the past, Apache Doris helped users greatly save the cost in computing and storage resources with many designs of ease of use. In the future, we will introduce a series of cloud-native capabilities to further reduce costs without affecting business efficiency, including:
- Lower storage costs: We will explore the combination of object storage systems and file systems on the cloud to help users further reduce storage costs, including better separation of hot and cold data, and migrate cold data to cheaper object storage or file system. Combining technologies such as a single remote replica, cold data cache, and hot & cold data conversion, we can ensure that query efficiency is not affected while saving up storage costs. This feature will be released in the first quarter of 2023.
- More elastic computing resources: We plan to separate storage and computing state and adopt Elastic Compute Node for computing. Since no data is stored, Elastic Computing Nodes have faster elastic scaling capabilities, which is convenient for users to quickly scale out during peak business periods, and further improve the analysis efficiency in massive data computing, such as lakehouse analysis. This function will be released shortly.
Hybrid Workload
Lots of users nowadays are building a unified analysis platform within the enterprise based on Apache Doris. On the one hand, Apache Doris is required to execute larger-scale data processing and analysis. On the other hand, Apache Doris is also required to deal with more analytical load challenges, such as real-time reports and Ad-hoc to ELT/ETL, log retrieval and more unified analysis. In order to better adapt to these cases, new features are about to be released in 2023, which include:
- Pipeline execution engine: Compared with the traditional volcano model, the Pipeline model does not need to set the concurrency manually, but instead, it can do parallel computing between different pipelines, making full usage of CPUs and is more flexible in execution scheduling, which improves the overall performance under mixed load cases.
- Workload Manager: It is also urgent to improve resource isolation and division capabilities. Based on the Pipeline execution engine, we will launch features such as flexible load management, resource queues, and isolation in shared services to balance query performance and stability in various mixed load cases.
- Lightweight fault tolerance: It can not only take advantage of the high efficiency of MPP structure but also tolerate errors to better adapt to the challenges of users in ETL/ELT.
- Function compatibility and UDF in multiple languages: At the same time, we will be more compatible with Hive/Trino/Spark function and support multiple UDF in the future to help users process data more flexibly. And data migration to Apache Doris will be easier than before.
Multi-model Data Analysis
In the past, Apache Doris was quite good at structured data analysis. As the demand for semi-structured and unstructured data analysis increased, we added Array and JSONB types from version 1.2 to support these data types naturally. In the future release, we will continue providing more cost-effective and better-performance solutions for log analysis cases, including:
- Richer complex data types: In addition to Array/JSONB types, we will increase support for Map/Struct types in the first quarter of 2023, including efficient writing, storage, analysis functions to better perform multi-model data analysis. In the future, more data types will be supported, such as IP and GEO geographic information, and more time series data.
- More efficient text analysis algorithms: For text data, we will introduce text analysis algorithms, including adaptive Like, high-performance substring matching, high-performance regular matching, predicate pushdown of Like statements, Ngram Bloomfilter, etc. The full-text search is based on the inverted index and it provides higher performance and is more cost-effective in analysis compared with that of Elasticsearch in the log analysis. These features will come out in early 2023. -Dynamic Schema table: In other databases, the schema is relatively static and DDL needs to be executed manually when the schema is changed. In recent cases, the table structure changes all the time, so we plan to launch Dynamic Table, which can automatically adapt to the Schema according to data writing without DDL execution, replacing manual adjusting. This feature will be released in the first quarter of 2023.
Lakehouse
With the development of data lake technology, analysis performance has become the biggest constraint to data-mining. Building analysis services on top of data lakes based on an easy-to-use and high-performance query analysis engine has become a new trend. In the last year, through many performance optimizations on the data lake, high-performance execution engine and query optimizer, Apache Doris has become extremely fast in analysis and easy-to-use on the data lake with a performance 3-5 times higher than that of Presto/Trino. In 2023, we will continue to go deeper, including:
- Easier data access: In version 1.2, we released Multi-Catalog, which supports automatic metadata mapping and synchronization of multiple heterogeneous data sources and is used for accessing data lakes. Delta Lake, Iceberg and Hudi will be better supported.
- More complete data lake capabilities: We provide incremental update and query of data on the data lake. Analysis result will be sent to data lake and the data from external tables will be ingested into internal tables. At the same time, Doris will also support multi-version Snapshot's read & delete and materialized views.
Real-time and storage engine optimization
The value of data will decrease over time, so real-time performance is very important for users. The Merge-on-Write data update in version 1.2 allows Apache Doris to be fast in both real-time updating and query. In 2023, we will upgrade the storage engine with the following:
- More stable data writing: Through a series of compaction operations and optimization of batch processing, resource cost is able to be saved. And through a new memory management framework, stability of the writing process will be improved.
- More mature data-updating mechanism: In the past, column updates were implemented through Replace_if_not_null on the Agg model. In the future, we will increase support for partial column updates with the Unique Key model, and data updates such as Delete, Update, and Merge.
- A unified data model: Currently, the three data models of Apache Doris are widely used in various cases. In the future, we will try to unify the existing data models to provide a better user experience.
Ease of use and stability
In addition to improving functions, simplicity, ease of use and stability is also the goal that Apache Doris has been pursuing. In 2023, we will dive deeper in the following:
- Simplified table creation: Currently, Apache Doris already supports time functions in table partitioning. In the future, we will further simplify Bucket settings to help users build models easily.
- Security: At present, a permission management mechanism based on the RBAC model has been launched, which makes user permissions more secure and reliable. Functions such as ID-federation, Row&Column-level permissions, data desensitization will be further improved in the future.
- Observability: Profile is an important means of locating query performance problems. In the future, we will strengthen the monitoring of Profile and provide visualized Profile tools to help users locate problems faster.
- Better BI compatibility and data migration solution: Currently, various BI tools can be connected with Apache Doris through MySQL protocol, and we will further adapt mainstream BI software in the future to ensure a better query experience. With the rise of emerging data integration and migration tools such as DBT and Airbyte, more and more users synchronize data to Apache Doris in this way. So we should provide support for these users in the future.
How to join the community
Last but not the least, we hope that more developers can participate in the community to jointly create a powerful database. There are 3 ways to participate in the community. First of all, users can subscribe to our developer mailing group through this address: dev@doris.apache.org, which is recommended by the Apache Way as well. You can send any related topics that you want to discuss with the community. Secondly, you can reach out to us virtually on developer's biweekly meeting. The biweekly meeting is held on Wednesdays at 8pm(UTC+8). The topic will cover new features, disclosure and development progress and more. Thirdly, the DSIP. DSIP is short for Doris Improvement Proposal. All Doris designed functions are recorded in this document. Both users and developers can follow and see detailed design and development of important functions on this Wiki.
Links:
Apache Doris Repository
https://github.com/apache/doris
Apache Doris Website
